

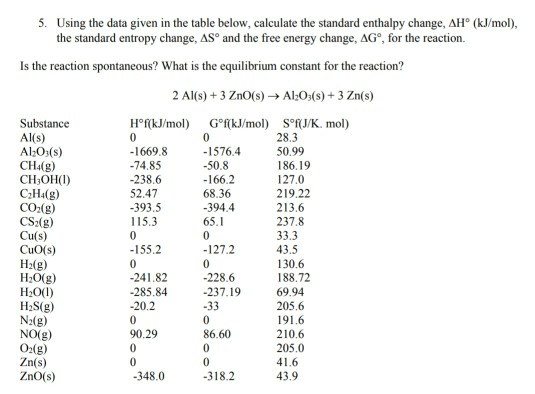
STANDARD ENTROPY TABLE FREE
C2H4 (g) + H2O (l) -> C2H5OH (l) Then, calculate the standard Gibbs free energy of the reaction, G°rxn. The standard enthalpy of the reaction, H°rxn, is 44.2 kJ·mol1. And so the whole point of having a two year was to show that if it there is, uh, coefficient in front of your, um, compound, you have to include it when you're calculating thes products minus reactant ce equations. Calculate the standard entropy, S°rxn, of the following reaction at 25.0 ☌ using the data in this table. 1 The Standard Molar Entropies of Selected Substances at 298.15 K (25C) Compound.
STANDARD ENTROPY TABLE PLUS
It cools the standard and B for C plus the standard entropy for D minus standard entropy for a plus two times the standard into B for B. A table like this can be used in much the same way as a table of standard enthalpies of formation in order to find the entropy change Sm for a reaction occurring at standard pressure and at 298 K. And so how does this look for this example? Reaction. All right, it's the sum of don't tow asked for reactant, but you do have to account for the stud commentary of your problem. And so Delta s not is gonna equal to the sum, uh, Delta s of products. See, I will say to be just, ah, emphasize the point here later on, goes to see plus de so reacted it's going to products. Write the mathematical equation that relates the standard entropy change in. Thus, the entropy decreases.So if you're given a table of standard entries, how are you supposed to calculate the entropy of the reaction? And so let's just dio a general or a reaction a plus. A table of absolute entropies (S) for selected substances is at the end of. There is more mixing involved, but the atoms of the gas go from being completely separated from each other to being closely packed with each other and the solvent. Entropy usually decreases when a gas dissolves in a liquid or solid.After mixing, they are completely interspersed within each other. Entropy usually increases when a liquid or solid dissolves in a solvent.īefore mixing, the solute and solvent are completely separated from each other.Two more patterns emerge from considering the implications of the first three. Therefore, the stronger bond will cause less disorder and less entropy. If you think of ionic bonds as springs, a stronger bond will hold the ions in place more than a weaker bond. Entropies of ionic solids are larger when the bonds within them are weaker (columns 3 and 4).Large, complicated molecules have more disorder because of the greater number of ways they can move around in three-dimensional space. Entropies of large, complicated molecules are greater than those of smaller, simpler molecules (column 2).The atoms in gases are far apart from each other, so they are much more disordered than either liquids or solids. Entropy has the dimension of energy divided by temperature, which has a unit of joules per kelvin (J/K) in the International System of Units. The atoms in liquids are still close together but they are free to move around with respect to each other, so they are more disordered. Entropy can be calculated for a substance as the standard molar entropy from absolute zero (also known as absolute entropy) or as a difference in entropy from some other reference state defined as zero entropy. On the nanoscale level, the atoms in solids are constrained to one position they can only vibrate around that position.
Therefore, q and DS are both positive and the liquid or gas has more entropy than the solid or liquid. This can be predicted from equation (1): heat must be put into substances to convert them from solid to liquid or liquid to gas. The entropies of gases are much larger than those of liquids, which are larger than those of solids (columns 1, 3, and 4).Some patterns emerge when these values are compared. In the table below are some excerpts from the Thermodynamics Table.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
